VA loans are among the most powerful mortgage choices available to veterans, active service members, and surviving spouses. The VA loan’s strength stems from a number of important financial perks that are not common in other mortgage types.
These benefits over other credit choices are a major reason why VA loan volume has increased significantly over the previous 15 years.
Last year, almost 750,000 VA loans were made nationally, totaling more than $250 billion for veterans and their families.
This historic benefit program has helped millions of veterans, service members, and military families realize their goal of homeownership. As a result, the use of VA loans has increased significantly since the Great Recession, and these government-backed loans are often regarded as one of the greatest mortgage options available today.
We questioned over 1,000 veterans and active military personnel. Here are the top reasons for selecting a VA loan among people who used their VA benefit:
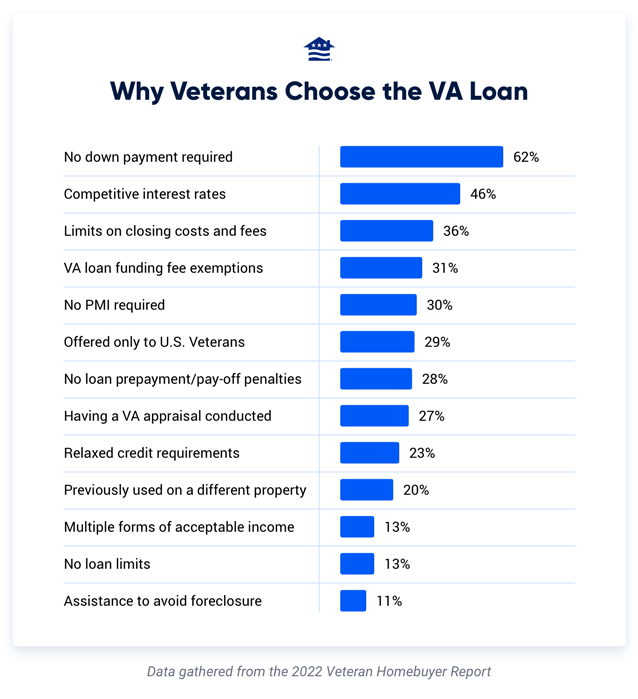
Let’s take a closer look at the most important VA loan benefits.
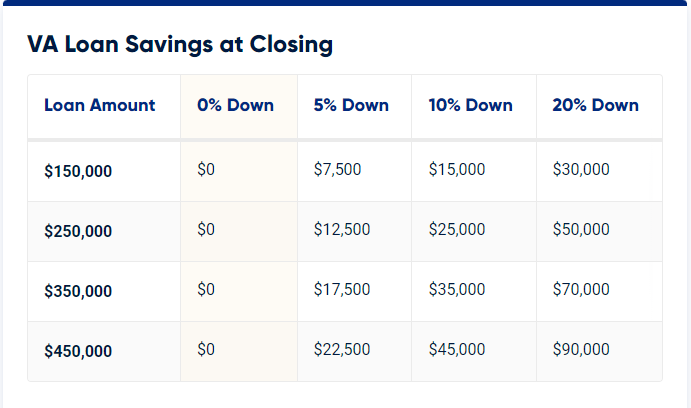
By far the most significant advantage of the VA loan is that qualifying Veterans can purchase without a down payment. This significant benefit enables veterans and military personnel to purchase houses without having to save for a traditional lump-sum payment.
Check your eligibility for a $0 down VA loan
The minimum down payment on an FHA loan is 3.5 percent, whereas conventional financing often requires 5 percent. On a $250,000 mortgage, a military applicant would need to provide $8,700 in cash for an FHA loan and $12,500 for a conventional loan. These may be large sums of money for the ordinary military borrower.
Service personnel who are always on the road may find it difficult to save money and create credit. Qualified applicants can finance 100% of the home’s worth with a VA loan, with no down payment required.
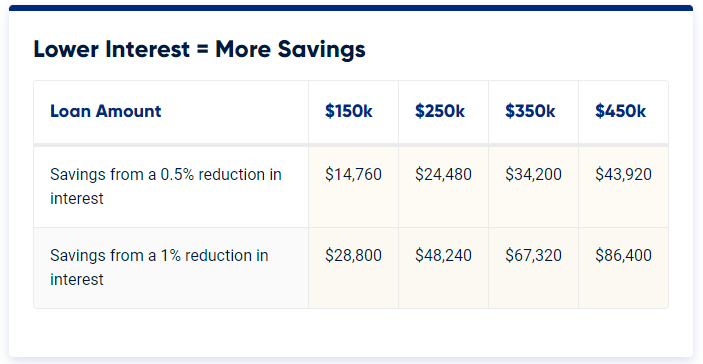
Take a look at the table below to discover how much you may save with the VA loan’s no-money-down perk.
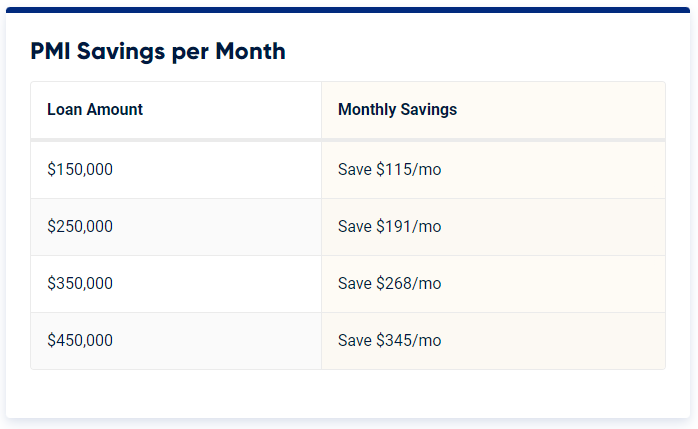
Private mortgage insurance (PMI) is insurance that protects lenders in the event of a borrower default. Many conventional lenders demand customers to pay private monthly mortgage insurance unless they can put down at least 20%, which can be difficult for many Veterans. Conventional borrowers will have to pay this monthly charge until they have 20% equity in their house.
FHA loans include their own type of monthly mortgage insurance.
Unlike conventional and FHA loans, VA loans do not require monthly mortgage insurance. With no private mortgage insurance, Veterans who obtained a VA loan last year will save billions of dollars in mortgage insurance fees over the course of their loans.
Without PMI, veterans may extend their purchasing power and save.
Another significant advantage of the VA loan program is that it offers the lowest average fixed rates on the market.
According to ICE Mortgage Technology statistics, VA loans have held the market’s lowest average 30-year fixed rate for the past six years.
VA interest rates are usually 0.5 to 1% lower than conventional interest rates. Lower interest rates help Veterans save money both monthly and throughout the life of their loan.
Because the Department of Veterans Affairs merely monitors the loan program and does not provide loans, it does not establish or enforce credit score minimums. However, most VA lenders utilize credit score criteria to determine a borrower’s likelihood of default.
Credit score minimums vary, although they are often lower than what borrowers require for traditional mortgages.
Veterans do not require near-perfect credit to obtain home financing at reasonable interest rates. VA loans are also more lenient when it comes to recovering from bankruptcy, foreclosure, or short sale.

It’s easy to continue right where you left off!
All mortgages include fees and closing charges, but the VA regulates how much Veterans may be charged for these expenditures. In reality, some costs and fees must be borne by other participants to the transaction. These precautions make homeownership more affordable for eligible purchasers.
VA borrowers can request that a seller pay all loan-related closing fees as well as up to 4% in concessions, which can include prepaid taxes and insurance, collection and judgment payments, and other expenses.
There is no assurance that the seller would agree to such request, but veterans may absolutely inquire during the bargaining process.
One of the most popular misunderstandings regarding the VA mortgage program is that it provides a one-time benefit.
Veterans who qualify for a VA loan can utilize this program indefinitely because the benefit never expires. Contrary to popular belief, you do not have to repay your VA debt in full to receive your benefit again.
Second-tier entitlement allows you to hold multiple VA loans at the same time.
Do not believe that since you used your house loan benefit decades ago, you are no longer eligible, or that because you have a VA mortgage at your present duty station, you cannot purchase with a VA loan when you PCS across the nation.
Begin your VA loan with SDVA Homes , California’s no #1 leading lender for veterans.
Paying off a house loan before it matures might result in a pre-payment penalty. This is because lenders pass up further opportunities to collect interest payments. The prepayment penalty allows financial institutions to reclaim part of the money.
Borrowers with a VA loan can return their mortgage at any time without incurring a prepayment penalty. Borrowers can evaluate future home purchases and refinancing alternatives without incurring a prepayment penalty.
For more than a decade, VA loans have been considered one of the safest loans available. That’s really astounding given that around 8 out of 10 homebuyers put no money down.
The VA mortgage program has emerged as a safe harbor for a variety of reasons, including the VA’s residual income requirements. The VA has also done an excellent job fighting for veterans in need and striving to keep them in their homes.
The VA guarantee program involves more than just getting veterans into houses. It also aims to assist veterans in maintaining their benefits.
The VA appraisal is a compulsory stage in the home-buying process that determines the property’s worth and condition. The appraisal serves two purposes: it determines the home’s appraised worth and ensures that it fulfills the minimal property criteria.
Establishing an appraised value ensures that the house is valued at “fair market value.” This indicates the home is priced similarly to other homes of the same size, age, and location. The VA appraisal provides borrowers peace of mind knowing their house was acquired at a fair price.
The VA’s MPRs aim to provide an extra safety net for veterans. These high-level property condition requirements are intended to assist Veterans purchase houses that are safe, sound, and clean.
Verifying income is a necessary step in the VA loan process. Lenders want to ensure that the potential borrower can comfortably afford their new monthly mortgage payment. Fortunately, many VA lenders accept several sources of income.
While salaries and wages are the most typical kinds, lenders may consider the following payments as effective income:
While these are some of the most prevalent effective incomes, other forms of military income, such as subsistence and clothing allowances, hazard pay, overseas pay, imminent danger pay, and others, may also be included.
Questions about whether you qualify? Speak with a home loan consultant to begin your VA loan .
Many veterans are astonished to learn how many financial alternatives the VA loan benefit provides. Veterans may use their VA loan benefit not just to buy a house, but also to make energy-efficient improvements, withdraw equity from their property, and refinance into cheaper interest rates.
VA purchase loans are one of the most popular financing alternatives for Veterans. Veterans utilize this form of financing to buy their principal house.
VA IRRRL loans, also known as VA Streamline refinances, are a great choice for Veterans looking to lock in a reduced interest rate or refinancing out of an adjustable-rate VA loan. This option is limited to Veterans with current VA loans.
A VA Cash-Out refinancing is for veterans who desire to withdraw equity from their property in exchange for cash. VA loan holders can utilize this money to pay off debts, make home modifications, or for emergencies. Veterans can use this option to refinance their non-VA mortgages.
VA EEMs are an alternative for Veteran homeowners to potentially cut their utility expenditures. Investing in energy-efficient modifications when purchasing a property can result in cheaper future heating, cooling, and other energy-related costs. Homeowners may be able to fund approved energy-efficiency upgrades via their loan.
VA loan limitations were once enforced for all Veteran purchasers, but this is no longer the case. Veterans with full VA loan entitlements can now borrow as much as they can afford, with no down payment required.
Previously, county-level constraints helped decide how much Veterans could afford before the zero-down loan program required a down payment. However, VA loan limitations remain in effect for veterans with reduced entitlement. In these circumstances, Veterans who want to buy beyond their entitlement limit must pay a fourth of the difference between that amount and the home’s buying price.
The VA Funding cost is a federal cost that must be paid with every VA loan. The money is sent straight to the VA to assist cover any losses and maintain the VA loan guarantee in effect. While most borrowers pay between 2.15 and 3.3 percent, certain veterans are completely free.
Veterans that are exempt from paying the funding fee include:
Assumability is an underappreciated characteristic of VA loans that can provide Veteran home sellers with a significant advantage during a period of rising mortgage rates.
With a VA loan assumption, the buyer effectively takes over the Veteran’s current mortgage, including the interest rate. VA homeowners can give prospective purchasers the opportunity to lock in ultra-low rates that are not available anywhere.
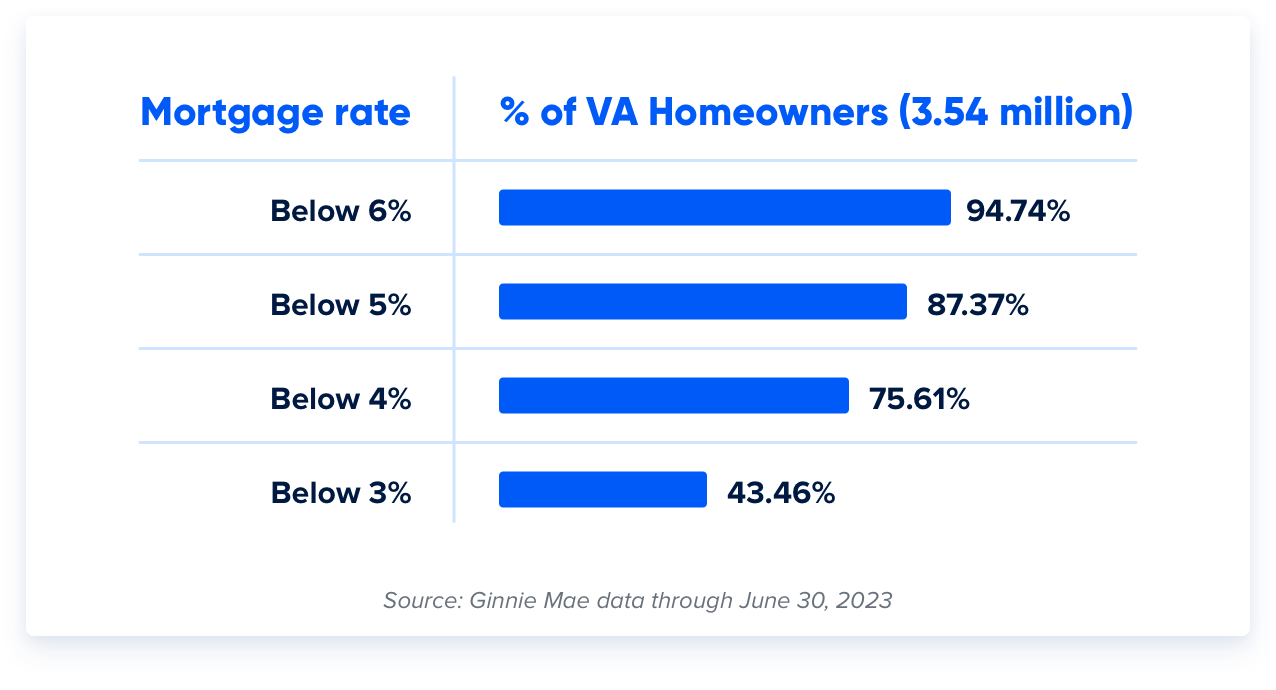
According to a study of Ginnie Mae statistics through June, nearly 9 out of 10 Virginia homeowners had a mortgage rate below 5%:
Loan assumptions have low rates and little closing fees because you are not receiving a new mortgage. Veterans and non-veterans alike can take out a VA loan as long as they follow servicer and VA criteria.
Veterans should note that their VA loan entitlement is still attached to the home unless the person taking over their mortgage is another Veteran who is substituting their entitlement for the homeowner’s. Otherwise, Veterans would have a more limited capacity to utilize their VA loan benefit, and may not be able to use it at all.
Every financial situation is unique; nonetheless, many people consider $0 down to be the most important VA loan advantage.
It depends on the particular homebuyer, but VA loans often feature cheaper interest rates and no down payment. VA loans also exclude mortgage insurance expenses, which might limit your purchasing power.
The biggest advantage for sellers is that VA purchasers are nearly as secure an investment as you can find. Furthermore, the VA does not obligate vendors to pay for anything on behalf of a VA buyer. Closing fees are always negotiable between buyer and seller.
SDVA Homes has been the top VA purchase lender for the past five years. Mortgages guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs are among the most valued advantages available to active duty military personnel, veterans, and their families.
NEXT STEP:
Start Your VA Home LoanCONTINUE READING: